The present use of ruled gratings for the absolute measurement of x-ray wave-lengths makes it necessary to investigate the possibility of systematic deviations from the simple formula for the diffraction from a perfect grating. A perfect grating is understood to have the following properties: (1) It is ruled on a continuum—its material has no atomic properties. (2) The optical properties of its material are completely determined by a refractive index (which may be complex). (3) It is ruled on a perfectly plane surface. (4) Its lines are truly parallel, identical, and uniformly spaced. (5) It is infinite in extent. (6) It is so oriented that the plane of incidence and diffraction is perpendicular to the rulings (this makes the problem two-dimensional). Of these properties, only (6) is non-essential and could be eliminated at the expense of a slight complication. The property (5) results in an infinite resolving power: theoretically, the resolving power of a finite portion of a perfect grating may be calculated in a manner which is discussed. It might seem that any derivation based on the foregoing simplifications could be no more general than the usual elementary derivation. However, the latter neglects the following factors: (a) The influence of multiple scattering; (b) Refraction, if the material of the grating is transparent. (This is really a particular case of (a)); (c) Shadows cast by one ruling on its neighbors; (d) Surface waves, similar to those arising on total reflection at a plane surface. In this case, these are the high order spectra for which sinθn1. A. H. Compton1 has given an elementary derivation which takes account of the factors (a), (b) and (c). The present calculation confirms his result that these factors do not influence the calculation of the wave-length, and extends it to include the factor (d).
See also:- Apostille services. Birth certificate apostille. New York apostille.
- There are two types of authentication for foreign documents. Georgia apostille. Atlanta apostille.

 Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
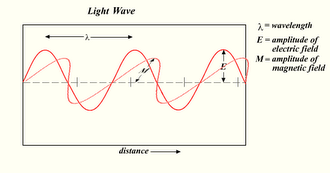 The theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation motivates the discovery of the Schrödinger equation, the equation that describes the dynamics of nonrelativistic particles. The motivation uses photons, which are relativistic particles with...
The theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation motivates the discovery of the Schrödinger equation, the equation that describes the dynamics of nonrelativistic particles. The motivation uses photons, which are relativistic particles with...